Lamina1 on Avalanche
The Lamina1 and Avalanche networks have been building together as official partners since October 2023.
As part of this collaboration, Avalanche provides the base-level consensus architecture and security mechanisms for Lamina1 to ensure digital assets and identities are safe and secure on the network. Meanwhile, Lamina1 has developed its own Layer 1 chain on top of Avalanche, building a stack of tooling capabilities and protocol integrations designed to facilitate the end-to-end development and distribution of open metaverse experiences.
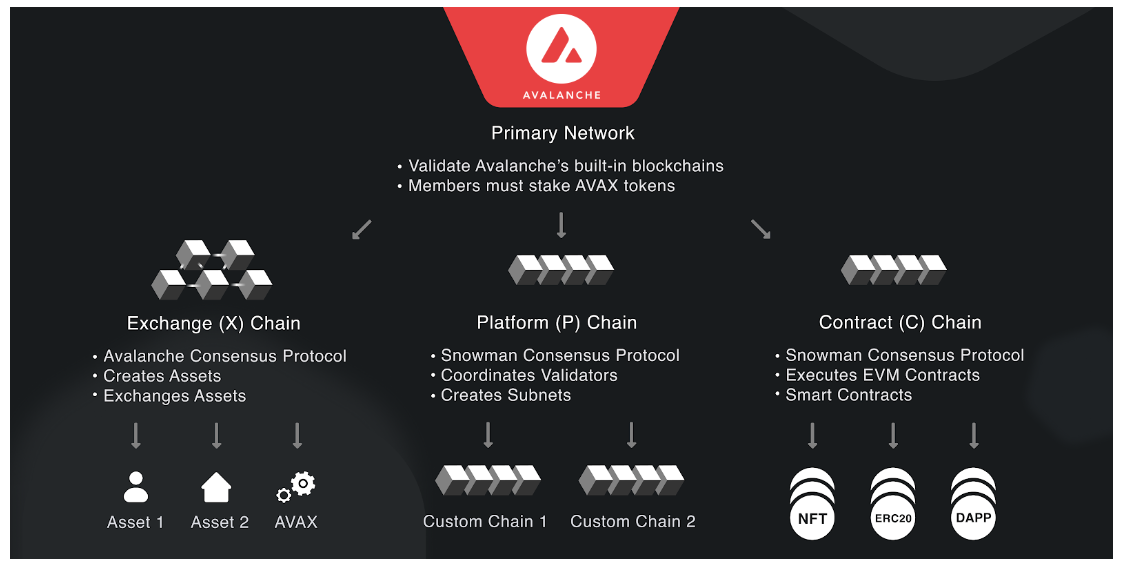
Per the Avalanche Platform Whitepaper, the Avalanche blockchain’s architecture is built to target three broad use-cases:
- Building application-specific blockchains, spanning permissioned (private) and permissionless (public) deployments
- Building and launching highly scalable and decentralized applications (dApps)
- Building arbitrarily complex digital assets with custom rules, covenants, and riders (smart assets)
As such, Avalanche is designed to support both decentralized applications and other autonomous blockchains and blockchain-based projects like Lamina1. Its core architecture is essentially a combination of its own native chains, virtual machines, and subnets powered by two consensus engines. This allows it to optimize scalability, speed, and interchain/network communication, again, making it the ideal foundation of a truly decentralized and interoperable web.
The basis of Avalanche’s innovative foundation for scalability are Subnets –– sovereign networks that define their own rules regarding membership and token economics on the Avalanche chain. As mentioned in the Lamina1 Architecture section above, Lamina1 essentially operates within a subnet, (or system of subnets) on the Avalanche platform, deployed by default by Subnet-EVM, a fork of Go-Ethereum that implements the Ethereum Virtual Machine, and supports Solidity smart contracts, as well as most other Ethereum functionality.
As a result, Lamina1 is compatible with familiar ETH method calls utilizing the Ethereum Virtual Machine as its “C” or “Contract” chain, alongside platform-specific X and P chains across the Avalanche network.
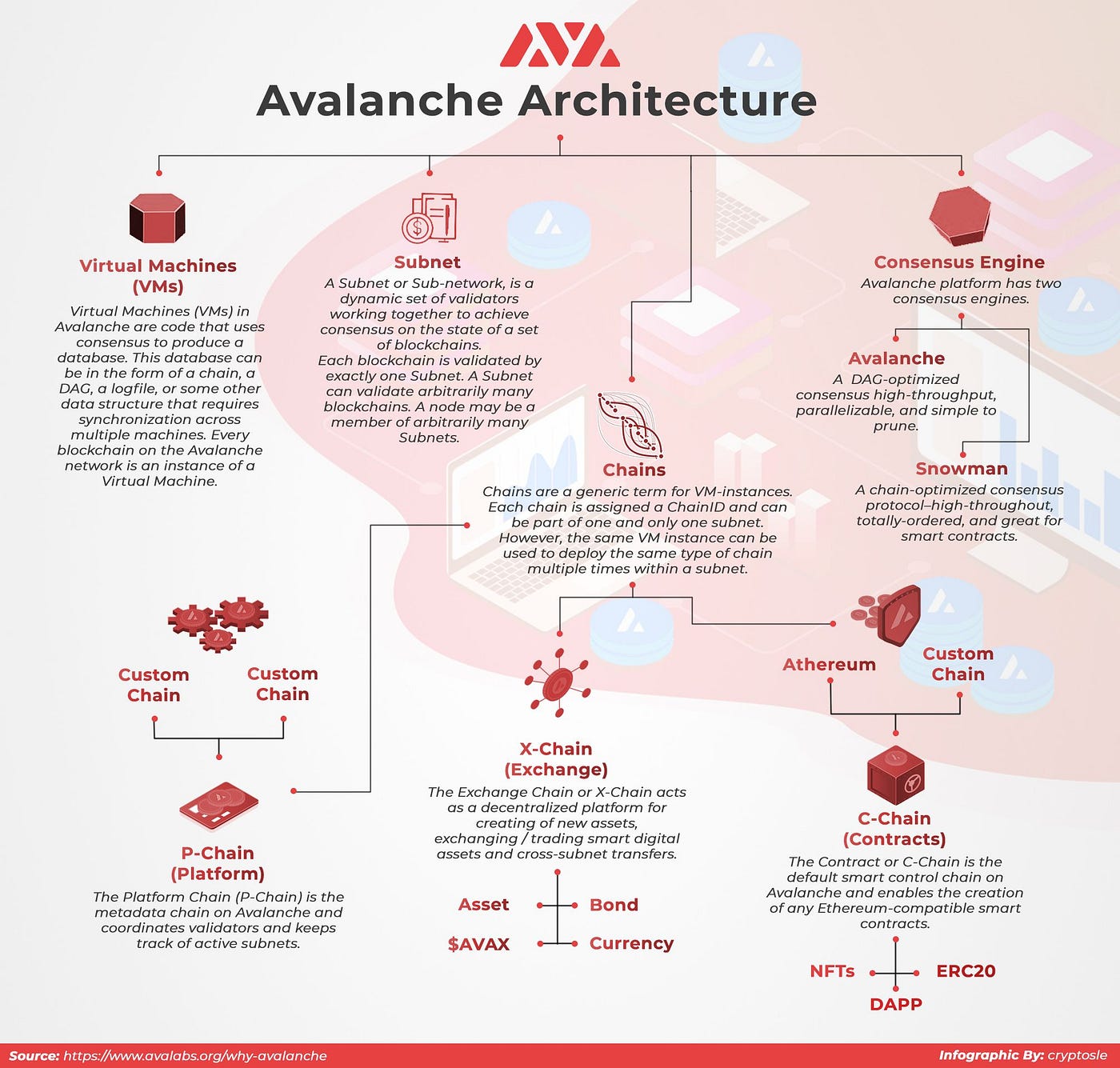
NOTE: In Mainnet, X/P chain functionality is largely abstracted for the average Lamina1 user, and Staking and Governance will take place directly on the Lamina1 Hub. If you’d like to learn more about how we built upon this underlying architecture during testing and development of the blockchain, see the Lamina1 Betanet section below.
Avalanche has extensive documentation on their platform as well. We recommend that anyone interested in learning more about the underlying architecture of Lamina1 and its chains familiarize themselves with the resources provided below.